Your kidneys play a critical role in keeping you healthy by filtering toxins, waste, and excess fluids from your body and into your urine. Glomerular disease is a group of conditions that, without treatment and management, can impact your kidney health and overall quality of life. Dr. Kanu and his patient-centered team at Texas Kidney Partners are committed to providing personalized care to ensure your kidneys function at their best for as long as possible.
What Is Glomerular Disease?
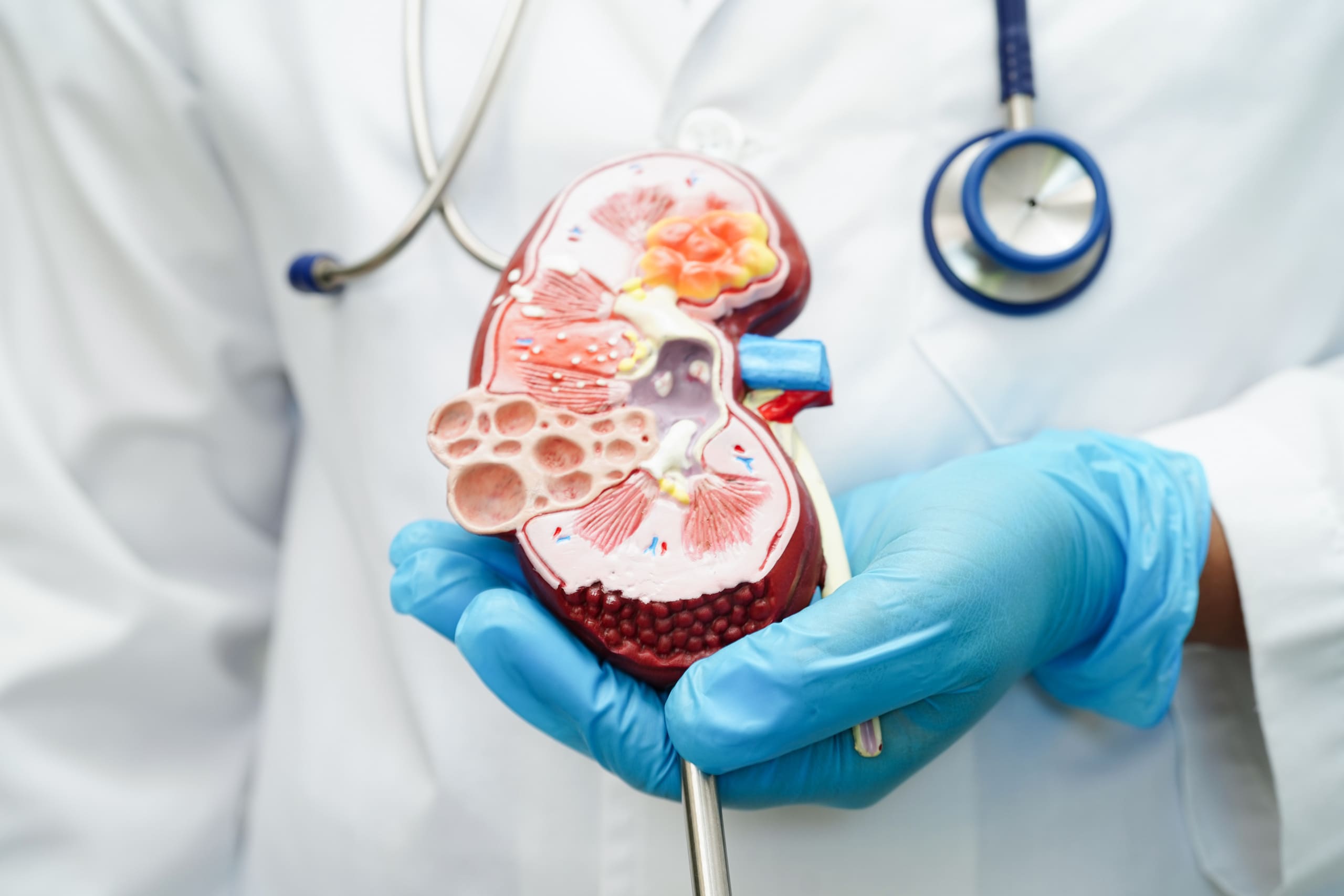
Your kidneys have microscopic filtration units known as nephrons. Each nephron has a glomerulus, a tiny cluster of looping blood vessels that filter waste, toxins, and fluid from your blood. There are approximately one million glomeruli in each kidney. Each glomerulus is connected to a small tube known as a tubule, where extra fluid and waste are expelled as urine. The urine then drains from the kidneys into the bladder through larger tubes known as the ureters.
Glomerular disease refers to conditions that cause damage to the glomeruli, interfering with their function. This can result in waste and excess fluids building up in the blood. Additionally, the damage can also lead to protein and sometimes red blood cells leaking into the urine. Loss of kidney function can lead to fluid accumulation, resulting in swelling of the face, hands, feet, or ankles. The disruption of the essential filtering process of the kidneys can lead to serious complications, impacting a patient’s health and quality of life.
What Are the Causes of Glomerular Disease?
Glomerular disease can result from various factors, including conditions that involve the body’s immune system. Some conditions, like IgA nephropathy, can trigger inflammation and damage. Other causes of glomerular disease include autoimmune diseases such as lupus and diabetic nephropathy, where high blood sugar levels progressively damage the delicate glomerular structures.
In addition to autoimmune and metabolic causes, genetic conditions also play a significant role. For example, Alport syndrome and polycystic kidney disease are genetic disorders that can lead to glomerular disease. Secondary factors such as hypertension and chronic viral infections can also cause stress on glomeruli, as can environmental factors, including exposure to certain toxins or heavy metals. Certain medications can also contribute to the onset of glomerular disease, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What Are the Symptoms of Glomerular Disease?
The following are some of the most common signs and symptoms of glomerular disease:
- Foamy or frothy urine resulting from excess protein (proteinuria)
- Signs of blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Noticeable swelling of the legs, ankles, feet, and around the eyes
- High blood pressure
- Changes in frequency of urination
- A general feeling of tiredness and weakness
- Brain fog and trouble sleeping
- Weight gain due to fluid retention
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Shortness of breath, muscle cramps, joint or abdominal pain
- Itchy skin, rash, jaundice, or darkening of the skin
If you experience any of these symptoms or have any other concerns, contact Texas Kidney Partners to schedule a consultation. Dr. Kanu will recommend personalized treatment options to keep your kidneys functioning their best for as long as possible.
How Is Glomerular Disease Treated?
The treatment for glomerular disease will depend on the underlying causes and the severity of the condition. The goals are to address the underlying causes, manage your symptoms, slow down kidney damage, and prevent complications, including kidney failure.
Dr. Kanu may recommend one or a combination of the following:
- Treating Underlying Conditions: If the glomerular disease is caused by an infection, autoimmune disease, or other condition, it’s important to treat the underlying concern.
- Blood Pressure Medication: Dr. Kanu may prescribe ACE inhibitors or ARBs to control high blood pressure, reduce protein loss in the urine, and prevent the progression of kidney damage.
- Managing Blood Sugar Levels: If you have diabetes, it is important to make dietary and lifestyle changes and keep blood sugar levels in check.
- Dietary Modifications: Treatment may include limiting sodium to reduce fluid retention and control blood pressure, restricting protein intake to reduce kidney stress, and controlling phosphorus and potassium intake to support kidney function.
- Exercise and Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can ease the burden on the kidneys and improve your overall health.
- Diuretics: These water pills help reduce swelling by removing excess fluid from the body.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants like corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide can suppress the immune system and reduce kidney inflammation.
- Statins: Statins can help lower cholesterol levels, which are often elevated in patients with some glomerular diseases.
- Anticoagulants: You may require anticoagulants for some glomerular diseases, particularly those with a risk of forming blood clots within the kidneys.
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): This procedure removes harmful antibodies from the blood that can be attacking the kidneys.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: It’s important to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and other factors affecting your kidney health.
- Dialysis or Kidney Transplant: If the kidneys fail, dialysis or a kidney transplant may become necessary.
Glomerular Disease Treatment Near Me in McKinney
Dr. Kanu and his team at Texas Kidney Partners are committed to providing personalized, compassionate care to help you maintain your kidney function for as long as possible. We will work alongside you to manage the symptoms and complications of glomerular disease to safeguard your kidneys and enhance your health and quality of life. Contact us at 469-613-2343 to schedule a consultation, or complete our online form to request an appointment today!